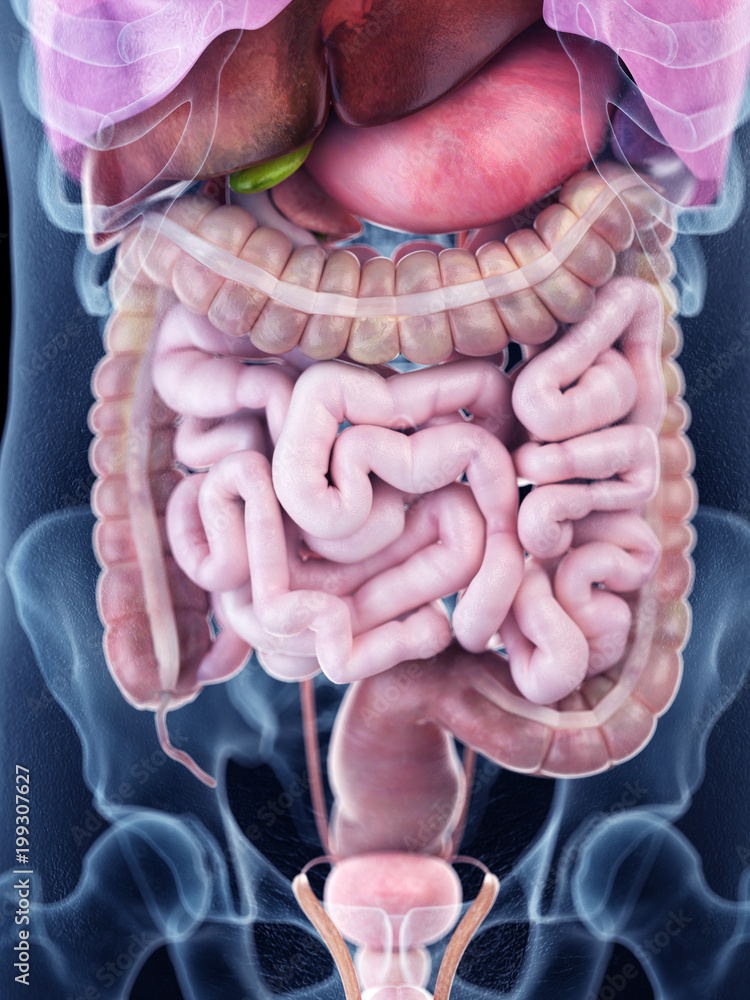
3d rendered medically accurate illustration of the human abdominal Biology Diagrams The stomach is an organ of the digestive system, specialized in the accumulation and digestion of food.Its anatomy is quite complex; it consists of four parts, two curvatures and receives its blood supply mainly from the celiac trunk.Innervation is provided via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus.. Thanks to the stomach, every human is technically capable of corroding metal and picking up The body (corpus) is the largest section of your stomach. In the body, your stomach contracts and begins to mix food. The antrum lies below the body. It holds food until your stomach is ready to send it to your small intestine. The pylorus is the bottom part of your stomach. It includes the pyloric sphincter. The stomach anatomy consists of four main sections and two curvatures. It gets its blood supply primarily from the celiac trunk. At the same time, its nerve signals come from the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus. In this article, we'll explore the stomach anatomy, its internal and external parts, and how its blood and nerves work together.
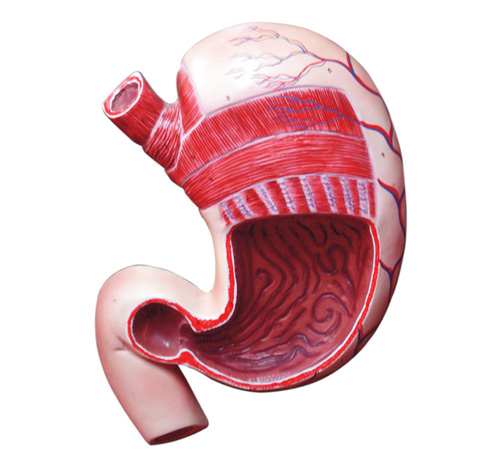
Anatomy. The stomach is a J-shaped, hollow organ in the digestive system designed for food storage, mechanical digestion, and chemical processing. [3] Below is a detailed description of its anatomy: Anatomy of the Human Body. 9th ed., Lea & Febiger, 1918. Boron, Walter F., and Emile L. Boulpaep.
Neurovasculature Biology Diagrams
The stomach, gallbladder, and pancreas are three of the most important digestive organs in the human body. These organs work together to produce and store secretions that digest our food into its most basic building blocks. Once digested, these small molecules pass into our intestines to be absorbed and to feed our body's tissues. The stomach also secretes a mixture of acid, mucus, and digestive enzymes that helps to digest and sanitize our food while it is being stored. Anatomy of the Stomach Gross Anatomy. The stomach is a rounded, hollow organ located just inferior to the diaphragm in the left part of the abdominal cavity. Anatomical Structure Divisions of the Stomach. The stomach has four main anatomical divisions; the cardia, fundus, body and pylorus: Cardia - surrounds the superior opening of the stomach at the T11 level. Fundus - the rounded, often gas filled portion superior to and left of the cardia. Body - the large central portion inferior to the fundus.
The first region of the stomach is called the cardia. It is the layer closest to the esophagus and it contains cardiac glands that secrete mucus. Mucus protects the delicate epithelial lining of many tissues in the human body. This region is followed by the fundus, which is the superior arch of the stomach. 3. Body (Corpus): This is the largest section of the stomach, located inferior to the fundus. 4. Antrum: This section lies below the body. 5. Pylorus: This is the bottom part of the stomach. It is a narrowing where the stomach joins the small intestine. The stomach's primary function is to digest food and send it to the small intestine.
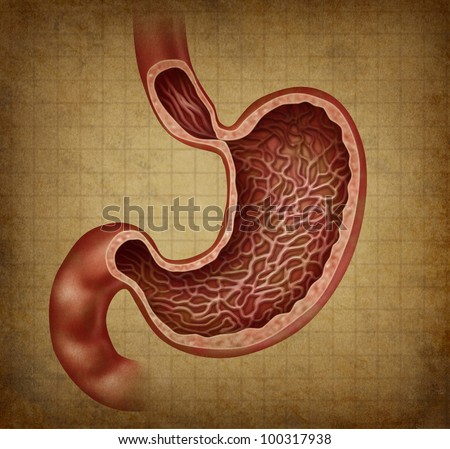
The Stomach: Anatomy and 3D Illustrations Biology Diagrams
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates.The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system.The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following the cephalic phase in which the sight and smell of food and the act of chewing are stimuli.

