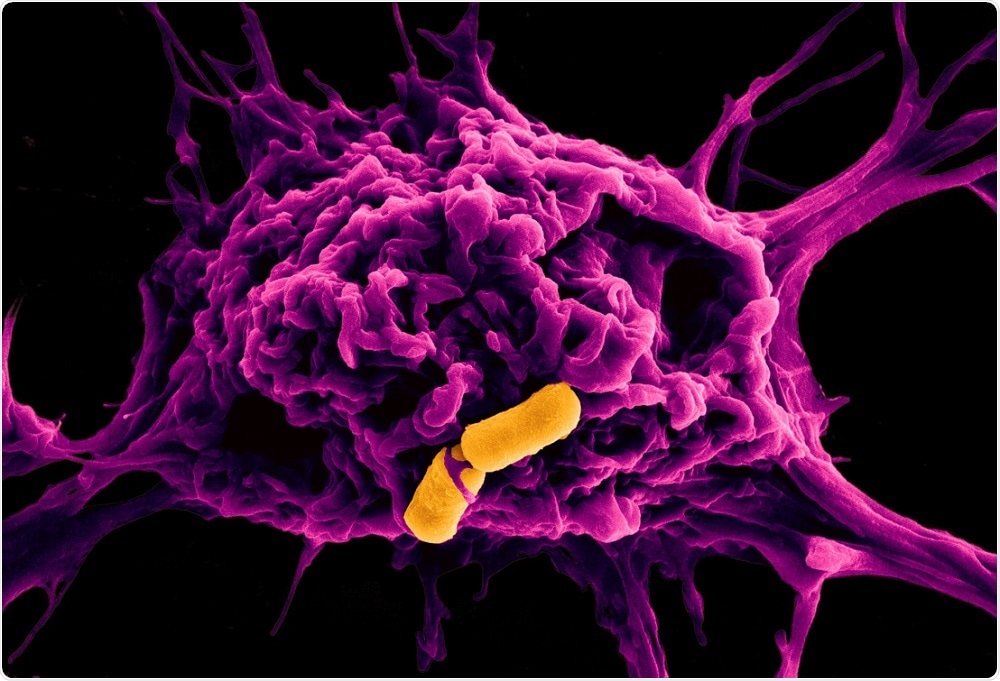
Bacteria In Food Biology Diagrams Food chains show interconnected food webs. Find out more with BBC Bitesize. The producers are bacteria which feed directly on the chemicals released from the vents and use a variety of Food chains and food webs are related but not identical concepts. While a food chain is a linear sequence of energy transfer, a food web is a more complex, interconnected network of food chains. Food webs better represent the complexity of ecosystems, where most organisms consume multiple types of food and are preyed upon by various predators.
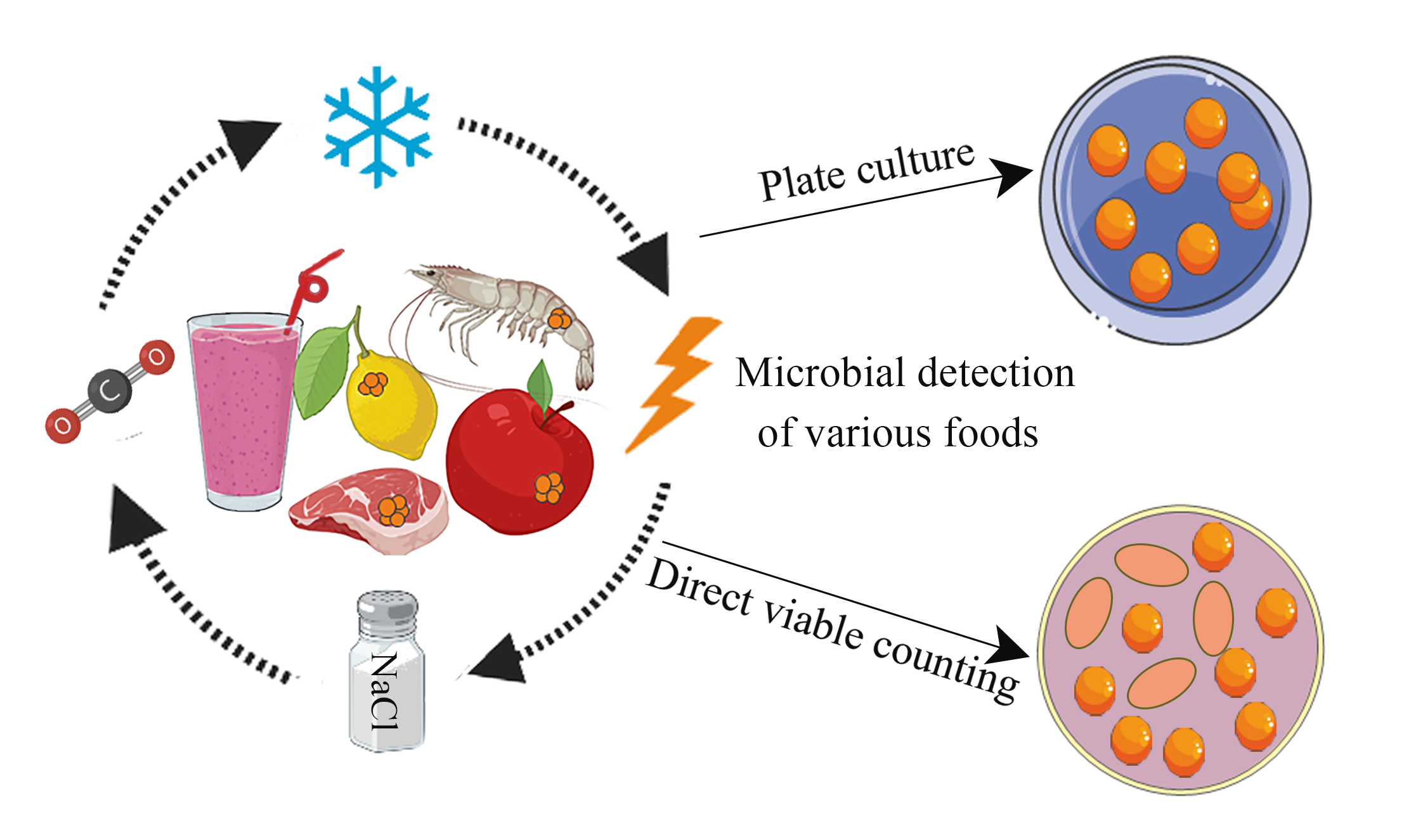
This Collection aims to explore the roles, behaviours and impact of bacteria throughout the food chain, from the farm to the fork, either cutting-edge research or comprehensive reviews may be considered for publication. Microbial ecology in agriculture, animal husbandry and production, fermentation processes, biofilm development, antimicrobial Q: What are the consequences for the food-chain and the safety of our food? A: When animals that have been given antibiotics are slaughtered, it is impossible to stop all the bacteria - both susceptible and resistant - in their intestine from being disseminated. So meat and other products that enter the food-chain can become contaminated. Continuous use and misuse of antibiotics have provoked the development of antibiotic resistant bacteria that progressively increased mortality from multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, thereby posing a tremendous threat to public health. followed by route of entry of drug-resistant pathogens into the food chain, and a plethora of

Review Stresses in the food chain and their impact on antibiotic ... Biology Diagrams
The main route of transmission between food animals and humans is via food products, although other modes of transmission, such as direct contact and through the environment, also occur. Resistance can spread as resistant pathogens or via transferable genes in different commensal bacteria, making quantification of the transmission difficult. A grazing food chain can be either predator or a parasitic type. In a predator grazing food chain, one animal consumes another animal. The animal that is eaten is known as the prey, and the animal that eats is called the predator. In contrast, plants and animals are infected by parasites in a parasitic grazing food chain. 2.

The food chain is a critical pathway for the dissemination of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, with sublethal environments in food processing potentially exacerbating or mitigating resistance development through cross-protection mechanisms. Numerous studies reviewed here highlight that disinfectants, bactericides, food additives, and common food
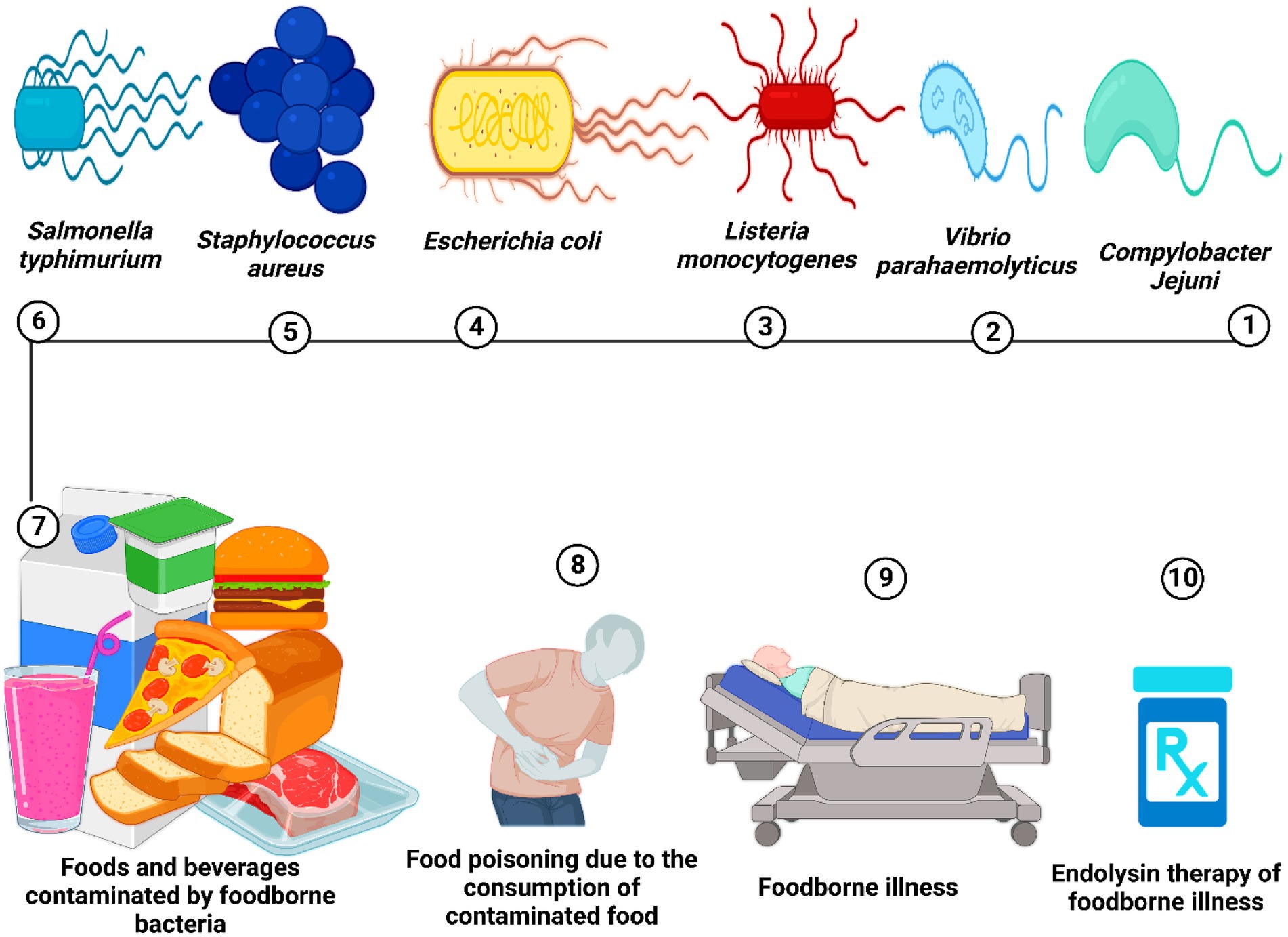
Bacterial Dynamics in the Food Chain: From the Farm to the Fork Biology Diagrams
4. Pathways of AMR in the Food Chain. Food is an excellent vehicle for spreading AMR spoilage and pathogenic bacteria. Notably, an increase in AMRB in food would have a negative effect on human health. The degree to which AMR is spread worldwide through the food supply may not be fully appreciated . AMRB may enter the food supply at any time Changes that have affected bacteria in the human food chain: Soil: Mass production of food has lead to short-cuts being adopted that leave out vital steps, in particular leaving pastures to rest with forage crops, legumes and animals. This slow composting of pastures returns organic matter and nutrients to the soil.