Biological Diversity Unit Biology Diagrams Reproduction: Asexual vs. Sexual. Cell division is how organisms grow and repair themselves. It is also how many organisms produce offspring. Cycle of Sexual Reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the production of haploid gametes by meiosis. This is followed by fertilization and the formation of a diploid zygote. The number of In this guide, we will explore the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction, comparing their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, we will look at different reproductive strategies using examples from both insects and plants. Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two gametes (reproductive cells) - one from each parent - to form a fertilised zygote. Sexual Reproduction. Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete (such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes (haploid) combines with another to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes (diploid). Sexual reproduction is the most common life cycle in multicellular
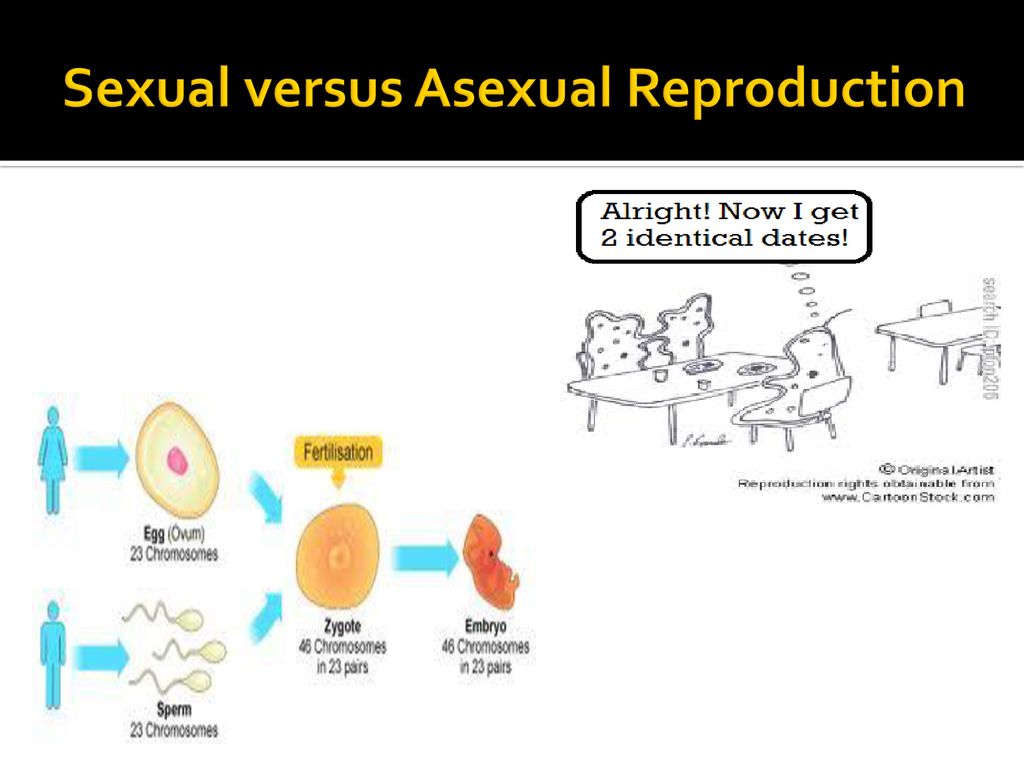
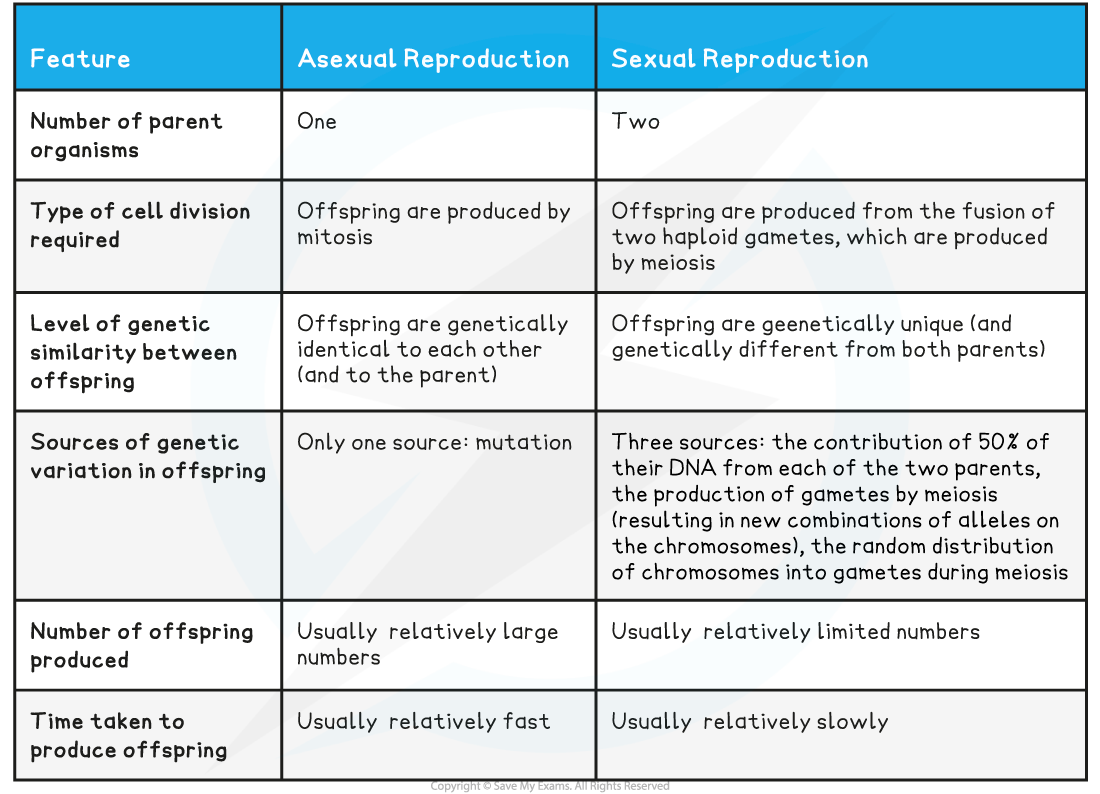
Animals produce offspring through asexual and/or sexual reproduction. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages. Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent because the offspring are all clones of the original parent. A single individual can produce offspring asexually and large numbers of offspring can be produced quickly. Sexual Reproduction. Sexual reproduction is the combination of reproductive cells from two individuals to form a third unique offspring. Sexual reproduction produces offspring with a different combination of genes. One must understand that sexual reproduction is a lot more complex than asexual reproduction. Both asexual and sexual reproduction offer unique advantages and disadvantages. The prevalence of each method across different species and environments highlights nature's diverse strategies for survival and propagation. Understanding these reproductive strategies is crucial for studying biodiversity, conservation, and evolutionary biology.
Chapter 29: Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Biology Diagrams
Main Difference - Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction. Sexual and asexual reproduction are two mechanisms that produce offsprings of the living organisms. During sexual reproduction, two types of gametes, known as male and female gametes, are formed inside the male and female reproductive organs, respectively.

Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction. Here are 16 differences between them. Sexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction involving a complex life cycle where the formation of new organisms occurs by the combination of genetic information from two different individuals of two different types (genders). While asexual reproduction only involves one organism, sexual reproduction requires both a male and a female. Some plants and unicellular organisms reproduce asexually. Most mammals and fish use sexual reproduction. Some organisms like corals and komodo dragons can reproduce either sexually or asexually. Compare and contrast asexual vs sexual reproduction. Learn the characteristics of each and explore the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction. Updated: 11/21/2023

