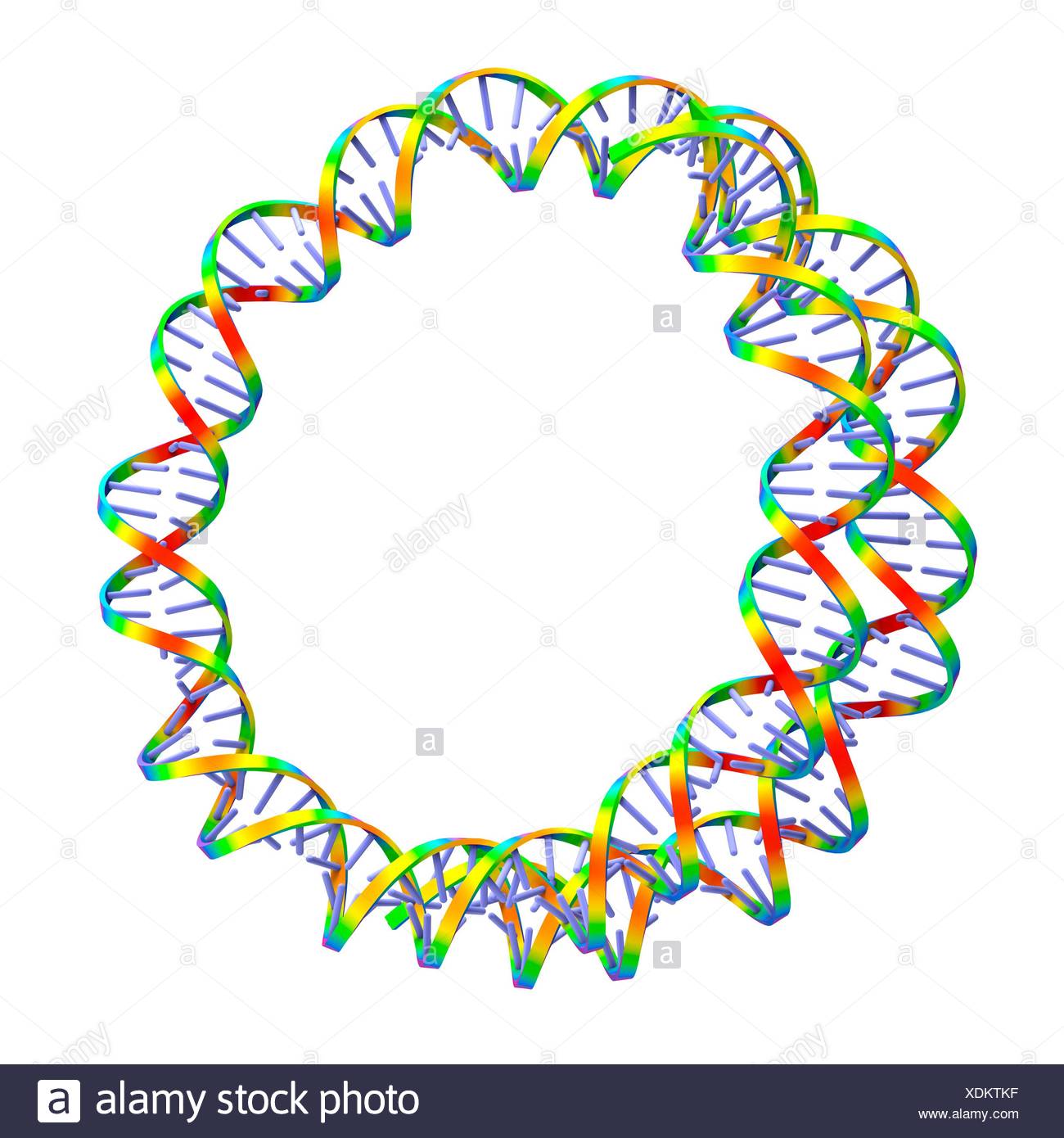
Circular DNA throws biologists for a loop Biology Diagrams Following DNA replication in the next cell cycle, the sister chromatids fuse once again and the BFB cycle can be repeated. Smith CA, Vinograd J. Small polydisperse circular DNA of HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972;69:163-78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90222-7. [Google Scholar] 29. Bertelsen AH, Humayun MZ, Karfopoulos SG, Rush MG. Molecular Introduction. EccDNA refers to a type of double-stranded circular DNA that is derived and free from chromosomes. In 1965, Alix Bassel and Yasuo Hoota first observed eccDNA in boar sperm using the electron microscope (Hotta and Bassel, 1965).From there, many efforts have been taken to figure out the features and functions of eccDNAs ().It is clear now that eccDNA is ubiquitous in eukaryotic

This semi-conservative process ensures each daughter mitochondrion receives an identical genome copy, linked to the cell cycle and influenced by cellular energy demands. Types Found In Cells. Circular DNA exists in various forms across different cellular environments, each with distinct functions and characteristics. These include bacterial Model of cell cycle stage effect on eccDNA formation. We propose that eccDNA generation by DNA repair depends on the cell cycle stage, as different repair mechanisms dominate during different cell cycle stages. Left: In humans, HR is mainly active during S and G2 phase, while a-EJ is active during S and G2 and remains active during M phase. An early study indicated that in hamster cells, BFB cycle could form ecDNA, resulting in unequal segregation and amplification of the adenylate deaminase 2 (AMPD2) Parsons L, Botstein D, Regenberg B, et al. Genome-wide purification of extrachromosomal circular DNA from eukaryotic cells. J Vis Exp (2016) 110):e54239. doi:

Unveiling the mysteries of extrachromosomal circular DNA: from ... Biology Diagrams
They found circular DNA in mammalian cells, boar sperms, and wheat embryos. 33 Before long, extrachromosomal DNA elements of diverse sizes and numbers were observed in mitotic human tumor cells. The BFB cycle can perpetuate through successive cell cycle, producing reverse repeat sequences in one daughter cell and terminating deletions in another. Single-cell extrachromosomal circular DNA and transcriptome sequencing (scEC&T-seq) was a plate-based method for parallel sequencing of circular DNAs and full-length mRNA from single cells
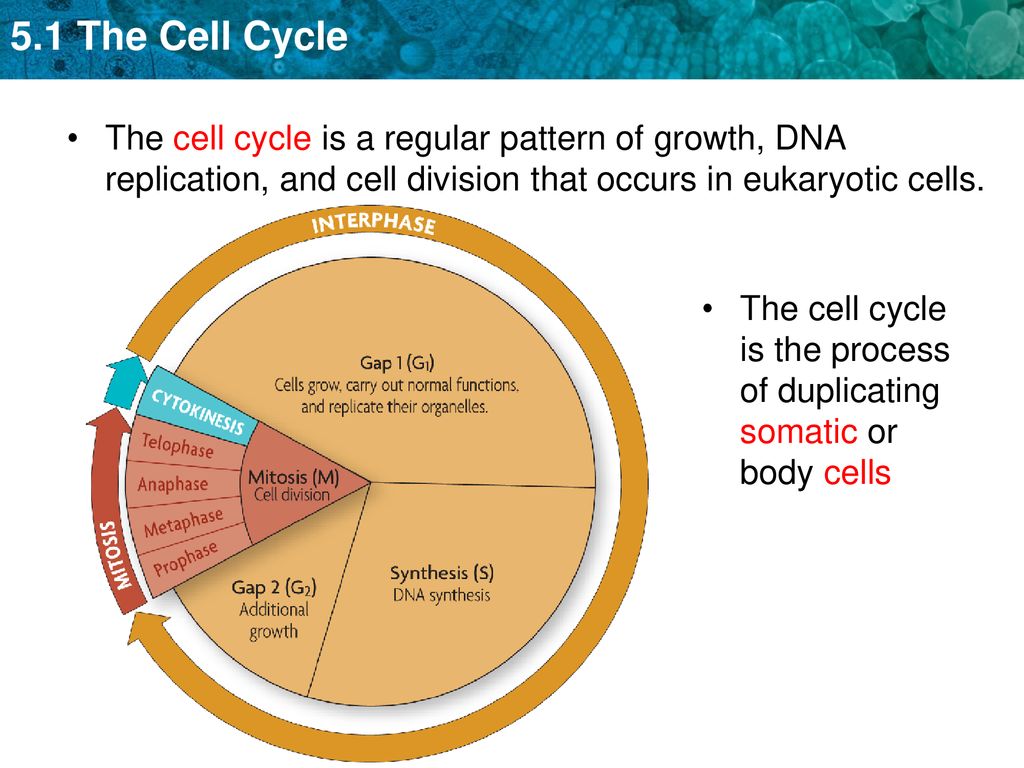
Total eccDNA abundance in cells can be up to a few hundred per cell. eccDNA molecules are also present in the circulation in cell-free form and offer the possibility to serve as blood-based biomarkers. In tumors, another type of extrachromosomal circular DNA can be detected, which appears to be exclusive to cancerous cells. Additionally, genomic stability is overseen by the cell cycle checkpoint and innate immunity surveillance. 84,85,86 Given that ecDNA is a manifestation of genomic instability, there is growing Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is a fascinating form of genetic material found outside the usual chromosomal DNA in eukaryotic cells, including humans. Since its discovery in the 1960s, eccDNA has been linked to critical roles in cancer progression and age-related diseases. This review thoroughly explores eccDNA, covering its types, how it forms, and its significant impact on diseases