Dna methylation Biology Diagrams While both DNA methylation and histone methylation involve the addition of methyl groups, their effects on gene regulation differ significantly. DNA Methylation Processes DNA methylation involves the addition of a methyl group (-CH₃) to the cytosine base of DNA, primarily at CpG dinucleotides. Effects of DNA methylation. DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification, i.e., heritable change in DNA without any modifications to the sequence of DNA. It alters expression of a gene during cell differentiation and causes a change that is heritable. Methylated modifications of DNA occur during the mitotic or meiotic division of the cell . The spectrum of effects produced by DNA methylation ranges from inhibition to enhancement of gene expression. Here basic terms and concepts in the study of DNA methylation are introduced. In

"DNA methylation in a normal cell vs. in a cancer cell"By Ssridhar17 - Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia About the Author: Lakna Lakna, a graduate in Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, is a Molecular Biologist and has a broad and keen interest in the discovery of nature related things. Understanding DNA methylation and its effects on gene expression is vital for advancing our knowledge in the fields of health and disease. It not only sheds light on the underlying mechanisms of gene regulation but also opens avenues for research into therapeutic interventions for genetic and epigenetic disorders. Mechanisms of DNA methylation However, when DNA methylation levels are partially or fully driven by genetic variants, DNA methylation levels and meQTLs effects can be tissue-specific or they can also be shared across tissues. Several studies have explored this question, focusing on how easily accessible tissues such as blood may be used as proxies for the indirect study of
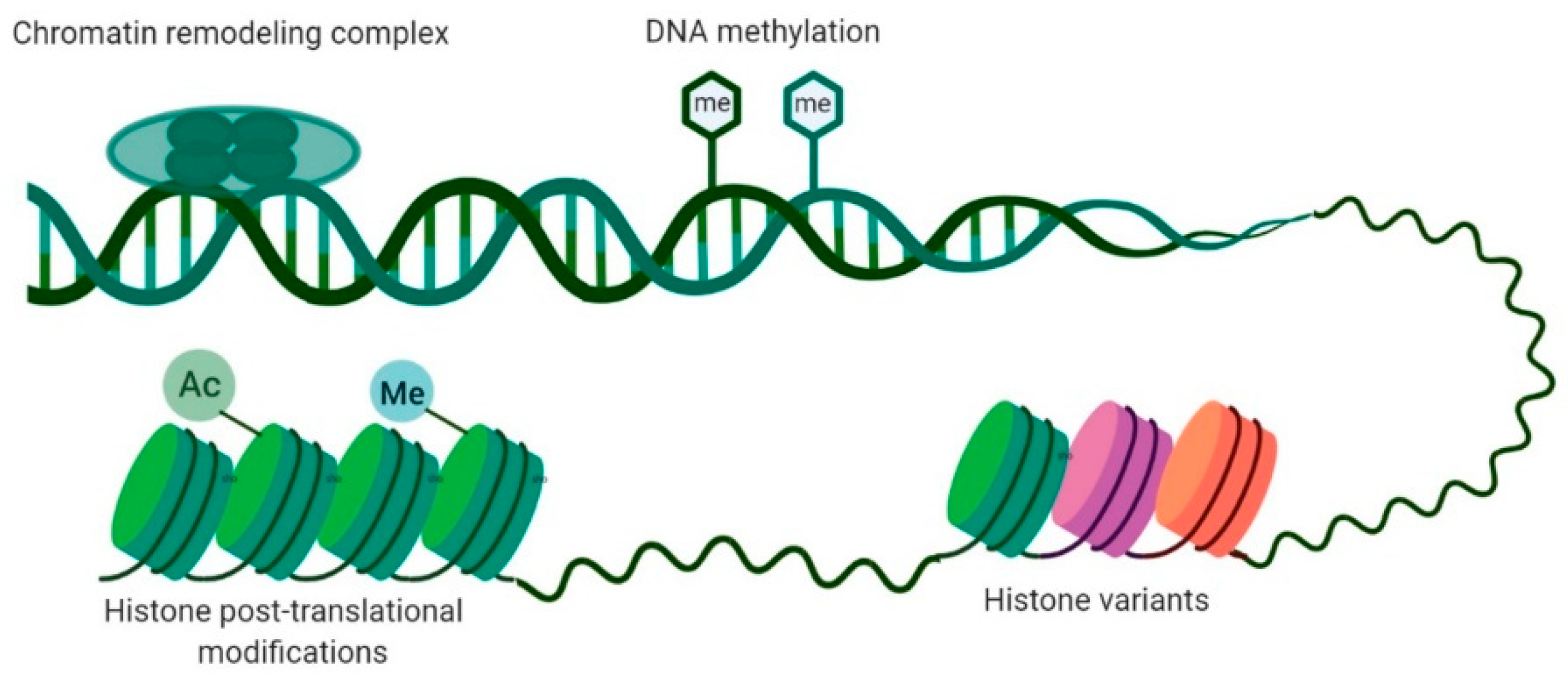
DNA Methylation vs Histone Methylation: Their Effects on Genes Biology Diagrams
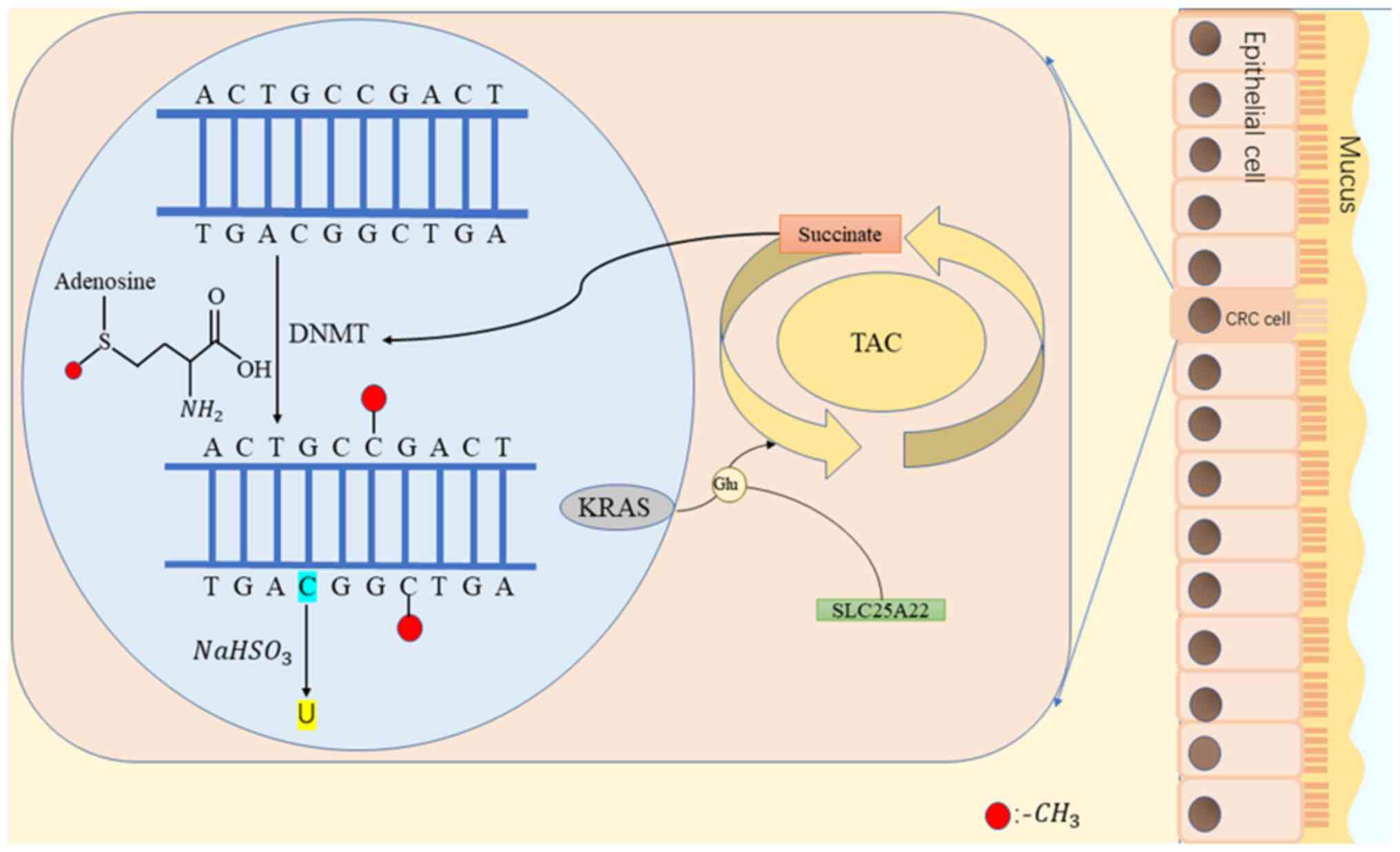
Other gene-neighbour effects like tissue-specific DNA methylation of small protein-encoding genes embedded in an intron of a larger dissimilar gene or of a tissue-specific enhancer in one gene linked to expression of the neighbouring gene . Figure 1. Open in a new tab DNA methylation pathways. A family of DNA methyltransferases (Dnmts) catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenyl methionine (SAM) to the fifth carbon of cytosine residue to form 5-methylcytosine (5mC).(a) Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are the de novo Dnmts and transfer methyl groups (red) onto naked DNA. (b) Dnmt1 is the maintenance Dnmt and maintains DNA methylation pattern during replication. DNA methylation has been employed for cancer detection for many decades, but new sequencing-based liquid biopsies that utilize cell-free DNA released from apoptotic and/or dying tumour cells into