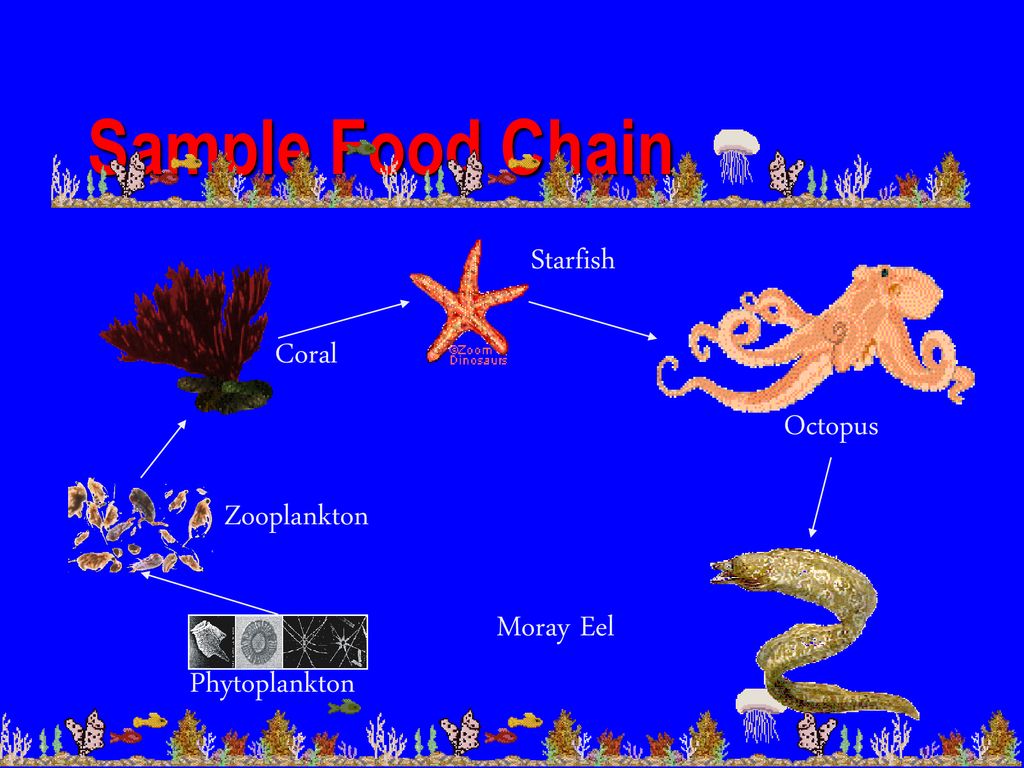
eating snail almost hunted to extinction could be Biology Diagrams Many fishes that inhabit tide pools, such as tide pool sculpin and young opaleyes, can breathe air at the surface—an adaptation that enables them to survive in oxygen poor water when the tide is out. Tide Pool Food Chains. A food chain is a diagram showing "who eats what" in an ecosystem. A single tide pool contains many food chains. Network3D images of food web networks of selected rock intertidal pools. a-food web with the highest S, b and c-food webs with average S, d-food web in the lowest S. Green nodes = basal taxa

algae, starfish plankton. Is a tide pool an example of a biome, ecosystem, or habitat? Explain. habitat, it is where many animals live and adapt. Create a food chain from the information in the case study using algae, limpets, crabs, and otters. otter eats crab, crab eats limpets, limpets eat algae

PDF 1.3 Intertidal Zone Biology Diagrams
What is a food chain and what organisms of the intertidal zone are interconnected? tide pools threaten inhabitants with wild changes in salinity, oxygen and temperatures, and , many creatures can be found in tide pools, including sea anemones, starfish, barnacles, hermit crabs, and even fish. This zone forms an extreme environment for Starfish acts as Keystone Species as they due to their presence in the ecosystem are known to keep tidal pools of the respective marine environment in an ecological balance. due to the absence of starfish, ocean food chain will surely become unbalance and also causing many other species to become endangered due to the low amount of prey or

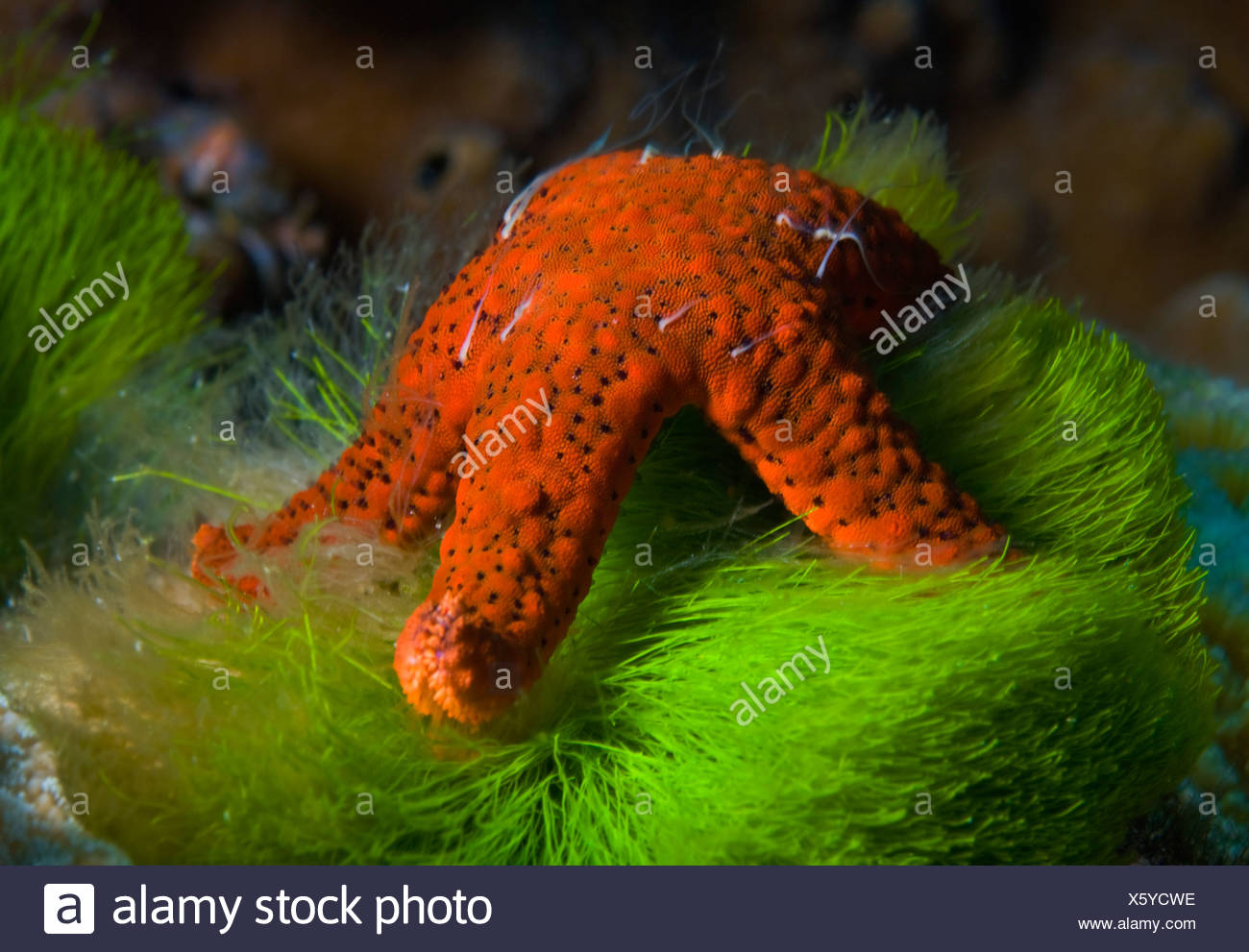
Waves Tides Sunlight Salinity Moisture What do starfish eat in tide pools? Starfish. Echinoderms make up the majority of marine creatures of tide pools, and the starfish seems to always take center stage. These invertebrates feed on microalgae, bivalves, snails, and sponges — all of which are readily available within the confines of a tide pool. Highly resolved food webs were compiled for 116 intertidal rock pools from cold, temperate, subtropical and tropical regions, to ensure a wide representation of environmental variability. The network properties of these food webs were compared to that of estuaries, lakes and rivers, as well as marine and terrestrial ecosystems (46 previously
How & Why Are Starfish Keystone Species? Biology Diagrams
The number of food web structural networks reported in the present work, n = 116, is remarkably higher than those previously reported for all other ecosystems combined, n = 46 ().The number of trophic species (S) observed in intertidal rock pools was considerably lower, 7-52, than that reported for all other ecosystems, 25-245, however such number of trophic species refers to much smaller

TIDAL POOL FOOD WEB Max Masleyev Tide pools are formed in saltwater-filled depressions located near an ocean or other body of saltwater. The name, "tidal pool" refers to their formation caused by the changing of the tides. Abiotic factors in tide pools include the terrain (rocks. Get started for FREE Continue.

