Evolution of haploid and diploid populations reveals common strong Biology Diagrams Many organisms fall in between these extremes, however, with biphasic (or haploid-diploid) life cycles, promises to shed light on when transitions occur between haploid dominance and diploid dominance and the major life history features associated with these transitions. In the next section, we explore how organisms with different ploidy
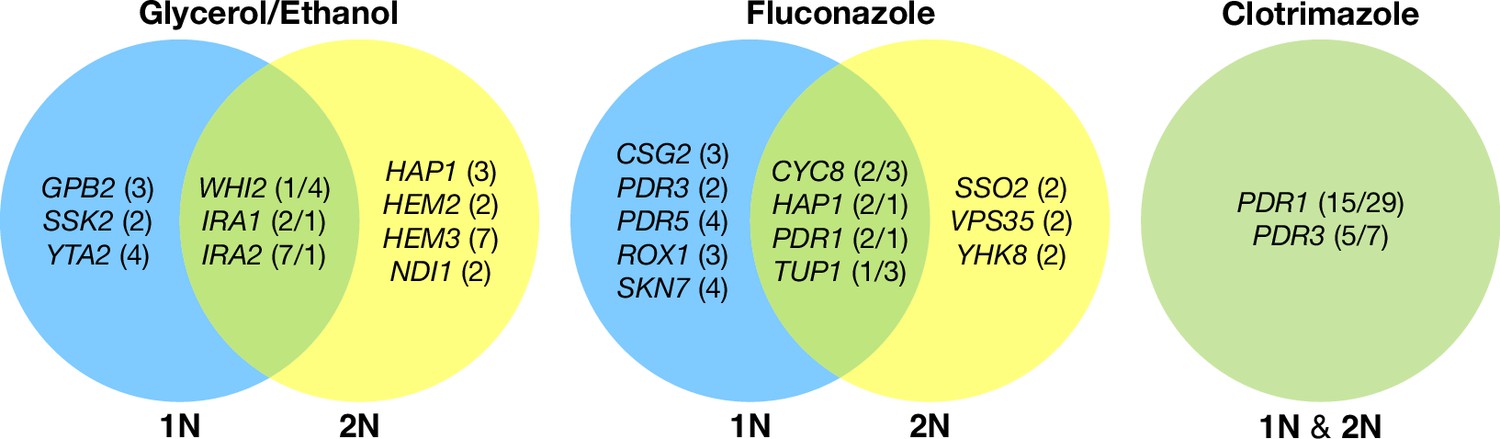
of haploid asexual females. Among plants, mitoses occur in both haploid and diploid phases, with the diploid phase predominating in ferns and seed plants. But polyploidy — having more than two sets of chromosomes — is very common among plants, and evidence is accumulating that all flowering plants have a polyploid history. In The transition from the haploid to the diploid phase appears to have some features beyond the mechanics of membrane fusion that are potentially widely conserved: In diverse organisms, homeodomain proteins are required to trigger zygote function ().First established in saccharomycete yeasts and then in basidiomycetes, this function of specific homeodomain-containing transcription factors has

The evolution of haploidy and diploidy: Current Biology Biology Diagrams
Plants have a life cycle characterized by alternation between two generations, haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte), where each phase develops a multicellular body (1, 2).The gametophyte produces gametes—sperm (or pollen) and egg cells—and may be the dominant photosynthetic generation, as in liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like _____ is the union of two haploid cells to form a diploid individual., In metaphase, how are chromosomes arranged on the axis?, Which process is referred to as reduction division? and more. The transition from haploid to diploid occurs_____ when gametes fuse during fertilization. Transition from haploidy to diploidy. June 1991; Nature 351(6324):315-7; DOI:10.1038/351315a0. To reveal how natural selection and genetic drift shape the evolution of haploid-diploid

The haploid-to-diploid transition in Chlamydomonas is masterfully controlled by the GSM1/GSP1 heterodimer, translating fertilization and gamete coalescence into a bona fide differentiation program. The fertilization-triggered integration of genes required to make related, but structurally and functionally distinct organelles—the vegetative As a direct consequence of sex, organisms undergo a haploid and a diploid stage during their life cycle. Although the relative duration of haploid and diploid phases varies greatly among taxa, the diploid phase is more conspicuous in all higher organisms. Transition from haploidy to diploidy Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):315-7. doi: 10.1038

