Fundamental kinematics laws of interstitial fluid flows on vascular walls Biology Diagrams The partition of fluid between the vascular and interstitial compartments is regulated by forces (hydrostatic and oncotic) operating across the microvascular walls and the surface areas of permeable structures comprising the endothelial barrier to fluid and solute exchange, as well as within the extracellular matrix and lymphatics. In addition to its role in the regulation of vascular volume Explore how interstitial fluid facilitates nutrient transport and cell communication, linking blood plasma and the lymphatic system. The fluid in the connective tissue spaces is called interstitial fluid. Interstitial fluid is important because it bathes cells, supplying them with essential substances and removing harmful ones. A space containing the fluid is known as an interstitial space. The connected spaces form the interstitium.

In anatomy, the interstitium is a contiguous fluid-filled space existing between a structural barrier, such as a cell membrane or the skin, and internal structures, such as organs, including muscles and the circulatory system. [1][2] The fluid in this space is called interstitial fluid, comprises water and solutes, and drains into the lymph system. [2] The interstitial compartment is composed

20.3 Capillary Exchange Biology Diagrams
It therefore attracts water. We can also say that the BCOP is higher than the interstitial fluid colloidal osmotic pressure (IFCOP), which is always very low because interstitial fluid contains few proteins. Thus, water is drawn from the tissue fluid back into the capillary, carrying dissolved molecules with it. Capillary Dynamics The four Starling forces modulate capillary dynamics. Oncotic or colloid osmotic pressure is a form of osmotic pressure exerted by proteins in the blood plasma or interstitial fluid. Hydrostatic pressure is the force generated by the pressure of fluid within or outside of capillary on the capillary wall.
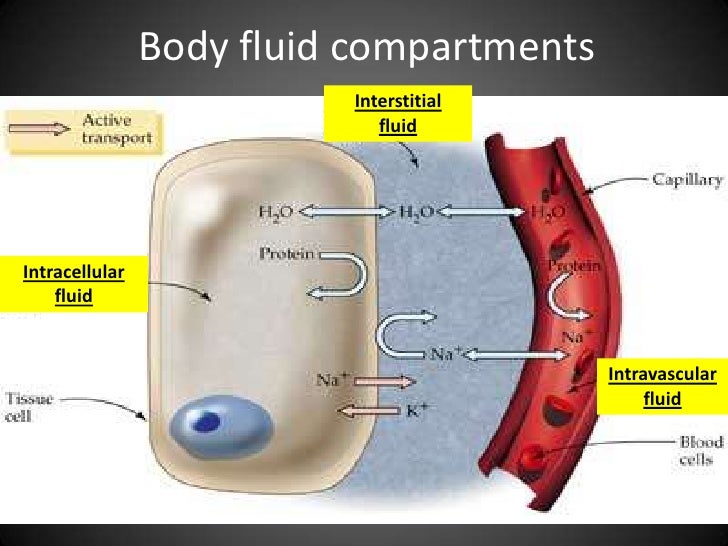
Fluid flowing across the capillary walls must cross the interstitial spaces between parenchymal cells to gain access to the lymphatic vasculature for subsequent return to the vascular system (Figure 1.1). The interstitium does not simply represent a passive conduit system for the flux of fluid and solutes, but also functions as a highly dynamic and complex structure whose physical properties
![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Interstitial Fluid Biology Diagrams](https://nursekey.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/F000418f041-004-9780323079334.jpg)
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology Biology Diagrams
Thus, fluid generally moves out of the capillary and into the interstitial fluid. This process is called filtration. Osmotic Pressure The net pressure that drives reabsorption—the movement of fluid from the interstitial fluid back into the capillaries—is called osmotic pressure (sometimes referred to as oncotic pressure). Thus, fluid generally moves out of the capillary and into the interstitial fluid. This process is called filtration. Osmotic Pressure The net pressure that drives reabsorption—the movement of fluid from the interstitial fluid back into the capillaries—is called osmotic pressure (sometimes referred to as oncotic pressure).

