Living Things Need Energy Biology Diagrams The third trophic level in the food chain, known as tertiary consumers, plays a crucial role in ecosystems by consuming secondary consumers and converting their energy into biomass. These apex predators hold primary consumers in check, ensuring balance and stability within the food web. From majestic lions preying on zebras in the African savanna to great white sharks hunting seals in the
+Energy.+Producer..jpg)
A tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. Tertiary consumers eat primary and secondary consumers as their main source of food. These organisms are sometimes referred to as apex predators as they are normally at the top of food chains , feeding on both primary and secondary consumers. Tertiary and Apex Consumers (Carnivores) Tertiary and apex consumers are carnivorous animals that reside on the top two trophic levels of the food chain. The organisms in this group include predators like the striped hyena, sand cat, fox, hawks and eagle, and cheetah. They feed on primary and secondary consumers. Those organisms perform the Importance of Tertiary Consumers. Tertiary consumers are more than just predators; they are vital components of a healthy ecosystem. Population Control: They regulate the populations of secondary consumers, preventing any one species from becoming dominant and disrupting the food chain. Ecosystem Stability: They contribute to the overall stability and health of the ecosystem by maintaining a
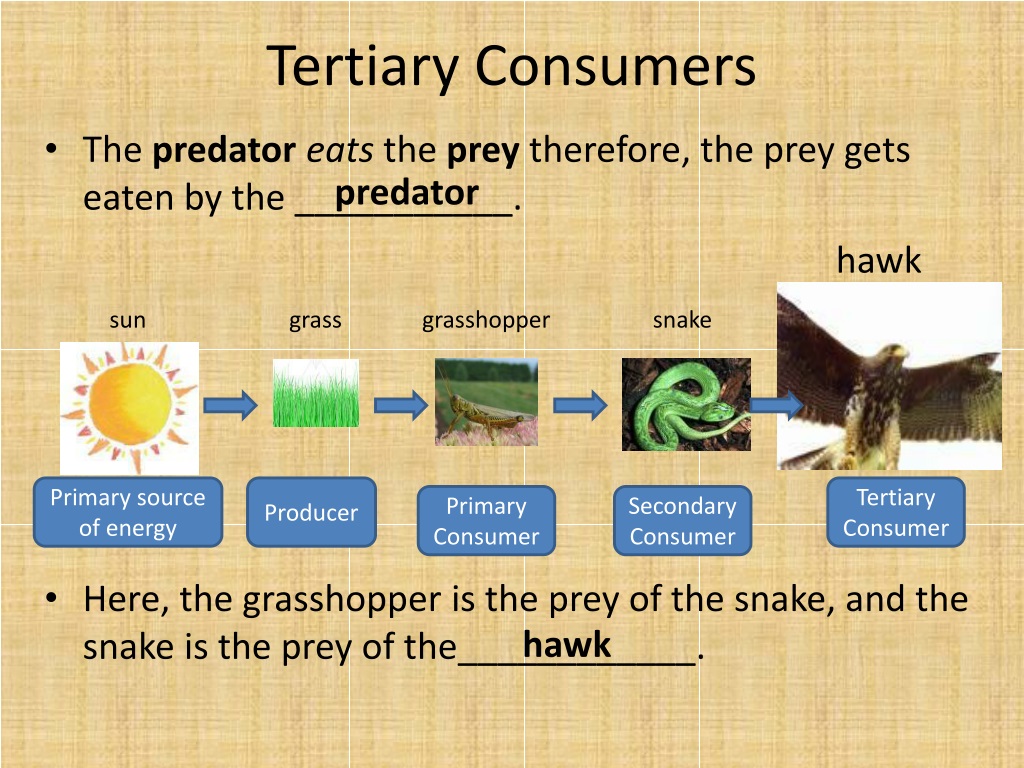
Tertiary Consumers: Apex Predators In The Food Chain Biology Diagrams
Producers are the first step in a food chain because they create their own energy. Primary consumers are the second step, and secondary consumers are the third. This makes a tertiary consumer the fourth step in the food chain because they consume secondary consumers for energy. Tertiary consumers can be: herbivores — organisms that eat plants Tertiary consumers often occupy the top trophic level, and so are predated by no other animals; in this case they are called "apex predators". However, when they die their bodies will be consumed by scavengers and decomposers. Sometimes in a food chain there is an apex predator above the tertiary consumer.
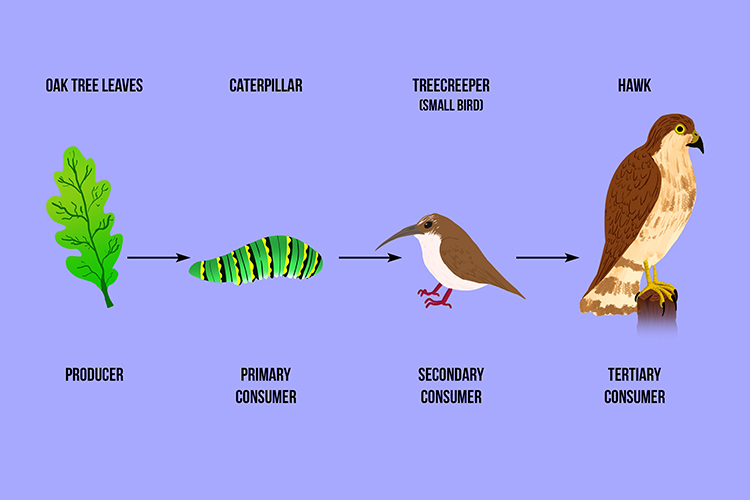
What is a Tertiary Consumer in a Food Chain? **A tertiary consumer is an organism in a food chain that feeds on secondary consumers or other tertiary consumers. It is at a higher trophic level and helps regulate the population dynamics of lower trophic levels, maintaining balance within the ecosystem.** Tertiary consumers can be found across The four levels in this food chain are primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and finally decomposers or phytoremediators. If you have any questions, don't be shy, and make sure to ask one in our comment section below. Tertiary Consumers - Tertiary consumers feed on secondary such as a pack of wolves. Caro says A food chain presents a unique, connected path of energy flow in an ecosystem, whereas the food web explains how food chains overlap. Both food chains and food webs, shares three types of organisms in a food chain: producers, consumers and decomposers. Explore more: Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web. Producers. Organisms that can

