Mitosis microtubules in cell division Flashcards Biology Diagrams Learn about microtubules, the cytoskeletal components that are involved in mitosis and other cell functions. Find out how microtubules are composed of tubulin subunits and how they can grow or shrink in size.

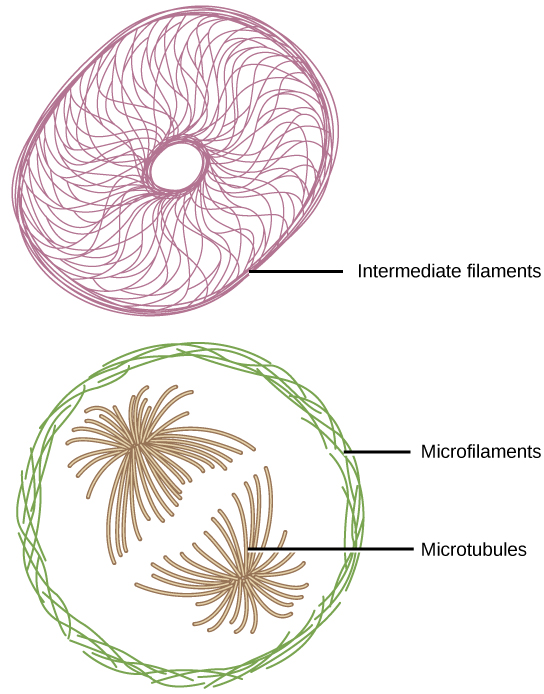
Learn about microtubules, the hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin that are part of the cytoskeleton. Find out how they are involved in cell movement, cell division, and transport in eukaryotic cells. The mechanical events of mitosis depend on the action of microtubules and mitotic motors, but whether these spindle components act alone or in concert with a spindle matrix is an important question. Understanding the mechanism of mitosis is a problem that has fascinated and frustrated cell biologists for over a century ( Mitchison and Salmon

Biology LibreTexts Biology Diagrams
Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\). A cell at metaphase. Microtubules are stained green, f-actin is stained red, and chromosomes, with centromeres lined up along the midline, are stained blue. Note the surrounding cells, which are not in mitosis, with their MT and MF cytoskeletons more overlapped. This photo released to public domain by the US government. Microtubules are cytoskeletal elements known as drivers of directed cell migration, vesicle and organelle trafficking, and mitosis. In this review, we discuss new research in the lens that has shed light into further roles for stable microtubules in The mitotic spindle is the cellular machinery responsible for chromosome segregation during mitosis, and it is comprised of hundreds of proteins. Gorbsky GJ, Borisy GG. Microtubules of the kinetochore fiber turn over in metaphase but not in anaphase. J Cell Biol. 1989;109:653-662. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.653.
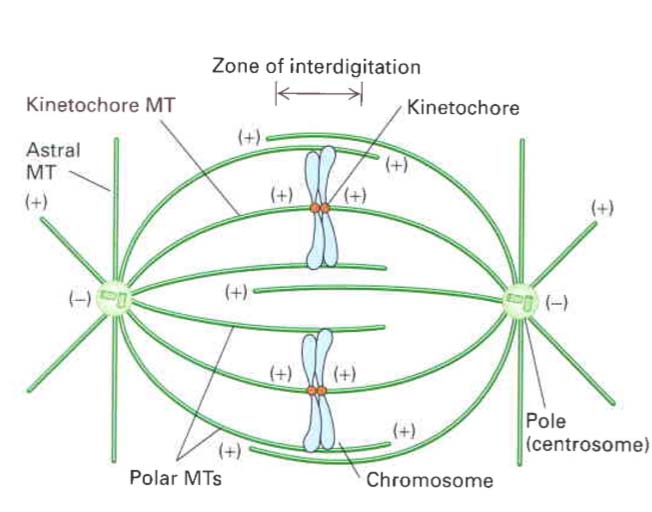
During mitosis, chromosomes are duplicated and divided evenly between two cells. The process begins with interphase and ends with cytokinesis. Polar fibers (microtubules that make up the spindle fibers) continue to extend from the poles to the center of the cell. Chromosomes move randomly until they attach (at their kinetochores) to polar

Definition, Function, Structure & Quiz Biology Diagrams
How does the cell-cycle control system trigger these dramatic changes in the cell's microtubules at the onset of mitosis? Figure 18-11. The half-life of microtubules in mitosis. Microtubules in an M-phase cell are much more dynamic, on average, than the microtubules at interphase. Mammalian cells in culture were injected with tubulin that had Mitosis is the process of cell division in which microtubules form a spindle that pulls apart the duplicated chromosomes. The web page explains the phases and mechanisms of mitosis, with illustrations and diagrams. During mitosis, microtubules similarly extend outward from duplicated centrosomes to form the mitotic spindle, which is responsible for the separation and distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells. The centrosome thus plays a key role in determining the intracellular organization of microtubules,