Regulation of Cell Division PowerPoint Presentation Biology Diagrams The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase (G0, G1, S, G2) and the mitotic phase (M). The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells undergoing cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA The eukaryotic cell cycle consists of four distinct phases: G 1 phase, S phase (synthesis), G 2 phase (collectively known as interphase) and M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). M phase is itself composed of two tightly coupled processes: mitosis, in which the cell's nucleus divides, and cytokinesis, in which the cell's cytoplasm and cell membrane divides forming two daughter cells.
Mitosis in an animal cell (phases ordered counter-clockwise), with G 0 labeled at left. Many mammal cells, such as this 9x H neuron, remain permanently or semipermanently in G 0.. The G 0 phase describes a cellular state outside of the replicative cell cycle.Classically [when?], cells were thought to enter G 0 primarily due to environmental factors, like nutrient deprivation, that limited the Learn about the phases of the cell cycle, including interphase and mitosis, in this Khan Academy article.

Cell Cycle: Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
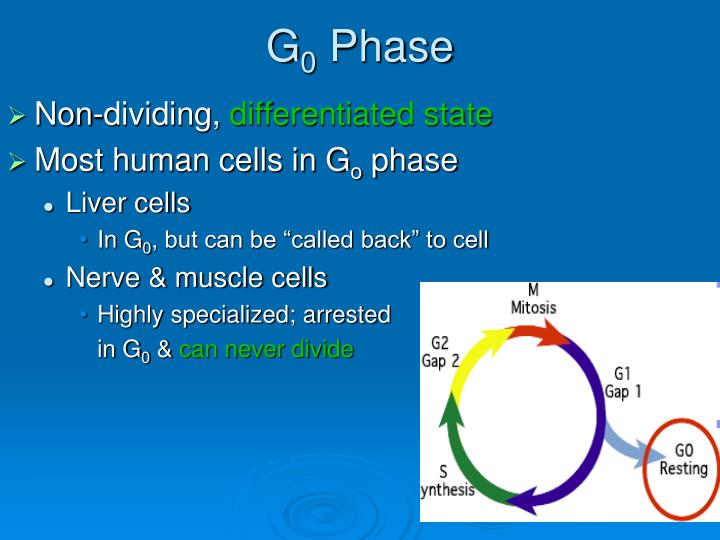
G0 phase. While some cells are constantly dividing, others are quiescent. These cells exit G1 and enter a resting state called G0. In G0, a cell is performing its function without actively preparing to divide. G0 is a permanent state for some cells, while others may re-start division if they get the right signals.

G 0 Phase. Not all cells adhere to the classic cell cycle pattern in which a newly-formed daughter cell immediately enters the preparatory phases of interphase, closely followed by the mitotic phase. Cells in G 0 phase are not actively preparing to divide. The cell is in a quiescent (inactive) stage that occurs when cells exit the cell cycle.

Khan Academy Biology Diagrams
Gap 0 Phase (G0) Gap 0 phase or G0 phase of the cell cycle is a period of time where the cell is present in a quiescent stage or resting phase, as it neither divides nor grows. Read More: Mitosis- definition, purpose, stages, applications with diagram 6. Cytokinesis. Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm into two halves, indicating the Interphase, the period preceding mitosis, is the longest phase of the cell cycle and has three distinct sub-stages. G1 Phase (Gap 1): This is the phase right after cell division. Cells increase in size, produce RNA and synthesize proteins. Importantly, this phase ensures that everything is in place for DNA synthesis to occur in the next phase. The cell cycle includes the G0 phase, G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and M phase, also known as mitosis. Interphase is the term used to refer to the G1, S, and G2 phases-- although G0 is sometimes

