Solved Part E Late ProphaseWhich is representative of Biology Diagrams Chromosome Condensation Mechanisms. The process of chromosome condensation during prophase II is a marvel of cellular organization, driven by a series of highly regulated molecular events. Central to this process are condensin complexes, which play a pivotal role in structuring and compacting chromatin.
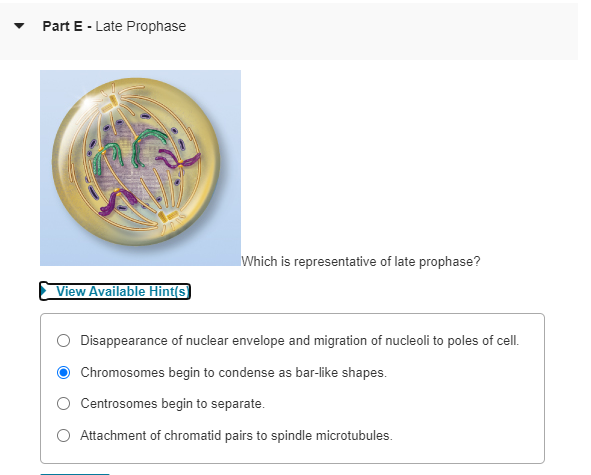
During prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. These are connected at a region called the centromere. The mitotic spindle also begins to form during this stage. Chromosome Condensation. Chromosome condensation is a crucial part of cell division. It happens during the

Condensation patterns of prophase/prometaphase chromosome are ... Biology Diagrams
Prophase: Chromatin Condensation Begins. As interphase draws to a close, the cell enters prophase, the first stage of mitosis. Here, chromatin condensation intensifies, transforming the diffuse chromatin into visible chromosomes. The nuclear envelope, which typically encloses the nucleus, disintegrates, allowing the chromosomes to interact freely.
However, degrees of chromatin condensation in prophase-prometaphase cells may vary along the chromosomes resulting in specific condensation patterns. We examined different condensation patterns (CPs) of prophase and prometaphase chromosomes and investigated their relationship with genome size and distribution of histone H4 acetylated at lysine

Visualization of early chromosome condensation Biology Diagrams
Instead, SMC2 associates throughout early and middle prophase chromatids, frequently forming foci over the chromosome exterior. Early prophase condensation occurs through folding of large-scale chromatin fibers into condensed masses. These resolve into linear, 200-300-nm-diameter middle prophase chromatids that double in diameter by late Here, I will zoom in on the process of chromosome condensation, which occurs during prophase. The compaction of chromatin to form the recognizable mitotic chromosome structures would serve little value until the evolution of the machinery for facilitating mitotic segregation. And yet, it is essential for mitotic division to proceed — that is
Prophase is the first step of cell division in mitosis. In the fifth and final phase of prophase I, diakinesis (from the Greek for "double movement"), full chromatin condensation has occurred and all four sister chromatids can be seen in bivalents with microscopy.

Nested Irreducible Complexity Biology Diagrams
Chromosome condensation is the key cytological landmark that classically defines the beginning of prophase (Flemming, 1882). Because interphase chromatin reorganization into individual mitotic chromosomes is extremely subtle at first, it is difficult to define exactly when prophase begins. Early prophase chromatin undergoes an orderly In HeLa cells, condensin I is excluded from the nucleus in interphase, binds to chromatin on nuclear envelope breakdown, and exchanges dynamically from chromatin throughout mitosis; condensin II is predominantly nuclear throughout the cell cycle and stabilised on chromatin at the onset of condensation in prophase . Both condensin complexes Condensin-driven condensation (left) in prophase leads to loop formation, which are subsequently compacted in axial and lateral direction. Histone-driven condensation (right) promotes local chromatin compaction mediated by interactions between neighbouring nucleosomes and controlled by post-translational modifications.

