Soma dendrite axon synapse neuron Images Stock Photos Vectors Biology Diagrams Neurons are electrically excitable cells that transmit signals throughout the body. Neurons employ both electrical and chemical components in the transmission of information. Neurons are connected to other neurons at synapses and connected to effector organs or cells at neuroeffector junctions. A typical multipolar neuron is comprised of soma or cell body, an axon, and dendrites. The axon is Neurons are interconnected through synapses, specialized junctions where the axon terminal of one neuron meets the dendrite or soma of another. These synaptic connections are dynamic, constantly forming and dissolving in response to learning and experience. This adaptability enables the brain to reorganize and adapt to new information. The synapse itself is the site of transmission from the pre-synaptic neuron to the post-synaptic neuron. The structures found on either side of the synapse vary depending on the type of synapse: Axodendritic. A connection formed between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another. These tend to be excitatory synapses. Axosomatic

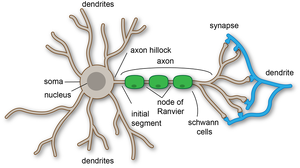
Figure 1.1. A typical neuron. Dendrites branch out from the cell body, where the nucleus is located. The axon hillock is located where the cell body transitions into the axon. The axon begins at the axon hillock and ends at the presynaptic terminal, which can branch into multiple terminals.

Neuroanatomy, Neurons Biology Diagrams
Synapse . Soma. Dendrites . Axon. Figure 3.7 The dendrites are the highly branched input sites of the neuron. They are named because of their resemblance to trees. Along the dendrites of some neurons, it is possible to see tiny protrusions of cell membrane that stick out from the main dendrite. These bumps are called spines. Spines can roughly
All neurons have three main parts: 1) dendrites, 2) cell body or soma, and 3) axons. Besides the three major parts, there is the presence of axon terminal and synapse at the end of the neuron. 1) Dendrites. They are specialized extensions that resemble the branch of a tree. Dendrites help to increase the surface area available for connections Neuron Anatomy Nerve Cell: Dendrites receive messages from other neurons. The message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron, then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. Next, the signal leaves the soma and travels down the axon to the synapse. Myelin sheaths cover the axon and work like A neuron is a nerve cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system. Neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which sends signals). Synaptic connections allow communication between neurons, facilitating the relay of information throughout the body.

3 Chapter 3: Cellular Anatomy of the Nervous System Biology Diagrams
When an action potential arrives at the synapse, it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft to bind to the receptors of the adjacent cell. Color the Neurons. Color the cell body and the dendrites blue. Color the axon (and myelin sheaths) red . Highlight the synapse with yellow. Terminal buttons are found at the end of the axon, below the myelin sheath, and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons. At the end of the terminal button is a gap known as a synapse. Neurotransmitters carry signals across the synapse to other neurons. When an electrical signal reaches the terminal buttons, neurotransmitters
..jpg)
