The Intertidal Zone on emaze Biology Diagrams What is the food chain in the intertidal zone? In the intertidal zone, the food chain begins with phytoplankton, microorganisms that use photosynthesis to create energy from the sun. These are usually consumed by zooplankton, which in turn is eaten by mussels, barnacles or other invertebrate. What do crabs eat in the intertidal zone? intertidal zone environment. TO introduce the biology and ecology Of the inter- tidal zone. TO examine organisms' special adaptations needed for existence on a rocky shoreline. To investigate life cycles and food chains where land and sea merge. To recognize that people are part of the tidal food chain Their gills provide the mussels with oxygen and help them capture food. When the tide is in, they open just enough to filter the seawater for tiny floating plants and animals. As one of the most abundant animals in the intertidal zone, mussels are also a key food source for others in the food chain.
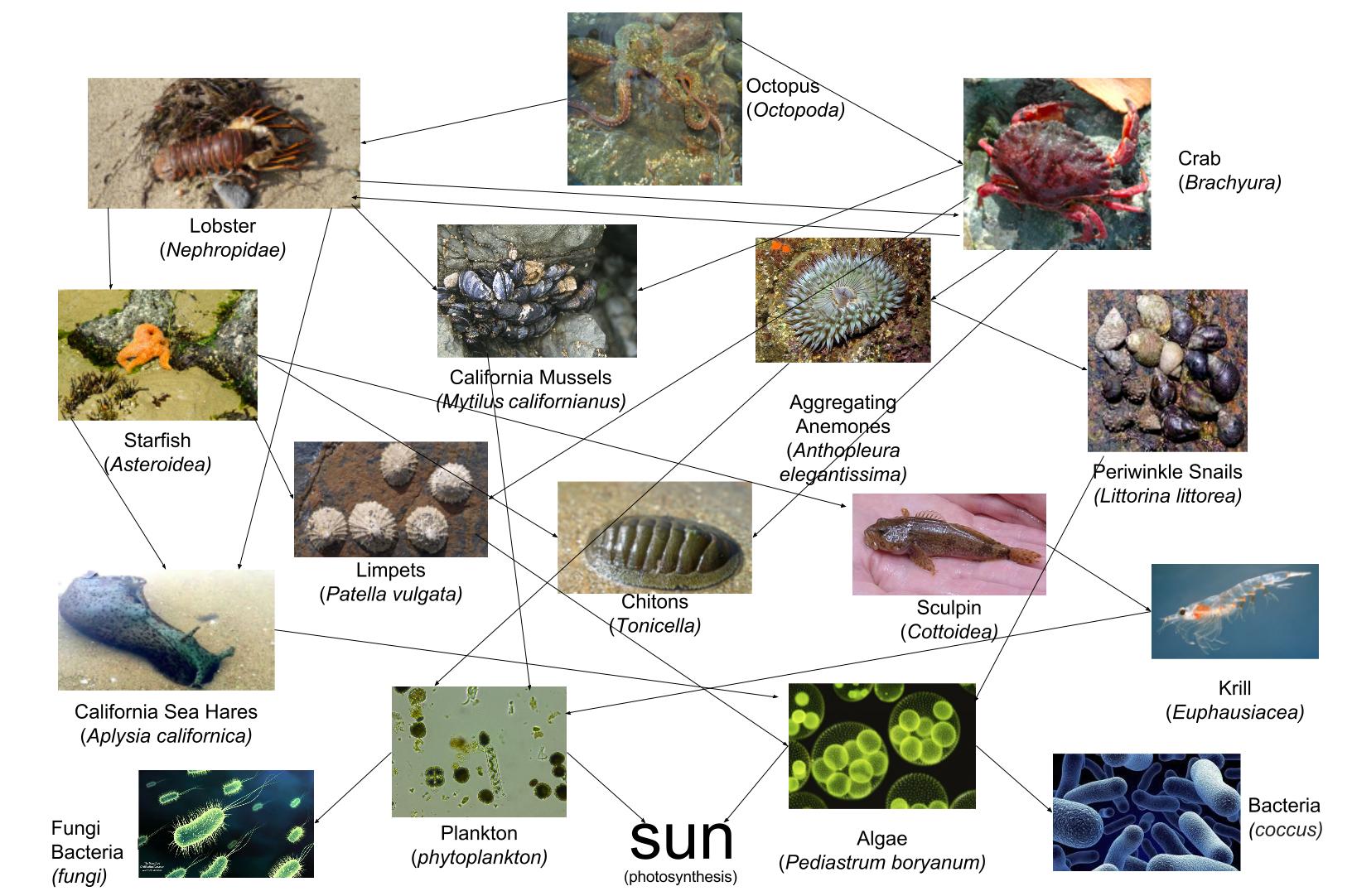
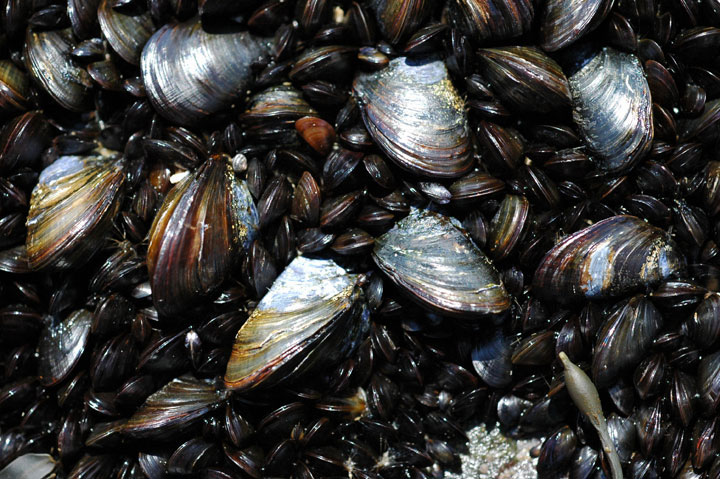
11.7 Rocky Intertidal Zones. 80. 11.8 Sandy / Mudflat. 81. 11.9 Antarctic Ecosystems. XII. Chapter 12: Marine Resources and Pollution. A food chain follows one path of energy and materials between species. A food web is more complex and is a whole system of connected food chains. A cross-sectional diagram of Mytilus californianus mussel This is life in the intertidal zone. The intertidal zone is the area on a shoreline between the high and low tides, and it offers an abundance of nourishment for marine life. Nutrients washed down from the land and gases churned by the waves feed algae and plankton, which form the base of the intricate intertidal food web. But intertidal life

Life in the Intertidal Biology Diagrams
In the intertidal zone, the food chain begins with phytoplankton, microorganisms that use photosynthesis to create energy from the sun. These are usually consumed by zooplankton, which in turn is eaten by mussels, barnacles or other invertebrate. Barnacles are usually eaten by whelks, a type of snail that in turn is preyed upon by sea stars.

First Chain Second Chain 1. lobsters eat clams 1. birds eat crabs 2. Food Chain - Representation of the movement of energy 1 mussel, 3 acorn barnacles and 1 goose neck barnacle) 2 predators, Pisaster and Thais Pisaster is the top predator, also eats 2 other species outside of the intertidal zone, a snail and a mollusc 13 species, 2 predators --> 15% are predators. Gulf of California 45 species of intertidal Blue mussels are eaten by humans, ducks, oystercatchers, bears and form an important link in the food chain. Look for them covering the rocks at low tides on beaches around the Kenai Peninsula. Butter Clams. If you see lots of oval, white-gray shells in the intertidal chances are they are Butter Clams. The 6" long shells are etched with many

U.S. National Park Service Biology Diagrams
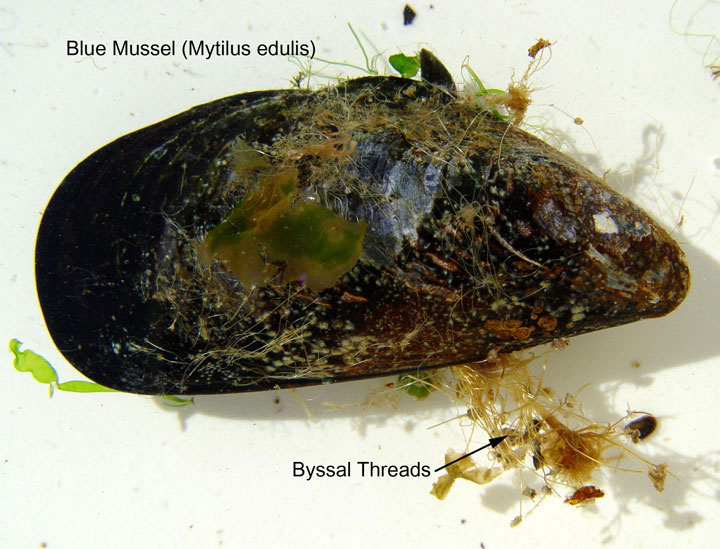
These mussels are found in quiet, sheltered areas in the mid-intertidal to subtidal water to 40 meters (132 feet) deep. Mussels produce sticky threads called byssus, that attach to rock substrates. Mussels are filter feed-ers and eat plankton. Although they are called blue mussels, they also vary in color from tan to brown as shown here.

